As the world embraces the digitalization of currencies and faster payment systems, cryptocurrencies have become a target for cybercriminals perpetrating all manner of hacks of which dusting attack is one of them.
Surprisingly, many owners of cryptocurrencies may not have come across the term “Dusting Attack or Dusting Scam” because it’s a relatively new scam technique.
Dusting attack was exposed for the first time in 2018 when a large-scale attack was launched on Litecoin users.
As speculators in cryptocurrency continue to increase their fortune, cyber-thieves are then extorting through cracks in digital wallets, therefore, exposing the blockchain network to more malicious activities.
We shall look at these attacks in much detail as we move on…
SEE ALSO: How to Flee These 10 Bitcoin Scams Now!
SEE ALSO: BitBox02 Hardware Wallets – Why You Should Buy One
SEE ALSO: Trezor One and Trezor Model T Bitcoin Hardware Wallets – Which is Better?
What is a Dusting Attack?
A dusting attack is simply a malicious activity where a person deliberately sends units of digital coins to the wallet of an unsuspecting person in other to steal their privacy.
A suspicious inflow of coins into the digital wallet could grant a hacker access through some malicious programs in other to de-anonymize the wallet owner or the wallet provider.
Dusting occurred first with Bitcoin before it became possible with altcoins provided the blockchain was publicly accessible.
The first dusting attack occurred in 2018 when a foremost wallet provider Samourai Wallet notified its users via social media that if they received small units of Bitcoins or other Altcoins as the case may be, they may be exposed to dusting attacks.
They were advised not to spend out of their wallets at the said time. Samourai implemented a Do Not Spend feature on their wallets automatically to arrest the situation.
The attacker aimed to de-anonymize the owners of the wallets and possibly perfect some linking of several hacked wallets together through a malicious program.
Samourai further hinted that the dust attacks were large scale perpetrated by a mining pool owner in an undisclosed location outside Russia.
Analyst uncovered that the large scale dusting attack was targeted at Litecoin users.
Binance analysts uncovered the large-scale dusting attack on Litecoin within 24 hours in June 2019. It was believed that the attack was to compromise users’ privacy.
#DUSTING #ATTACKS ON #LITECOIN HAPPENED AS #BINANCE CLAIMS:
— altrady (@altradyapp) August 11, 2019
“Approximately 5 hours ago there was a large-scale dusting attack on $LTC @litecoin users.”@binance #LTC #BinanceExchange #Hack #Scam #CryptocurrencyTrading pic.twitter.com/3mUO1vh8sY
SEE ALSO: World Most Popular Hardware Wallet-Ledger Nano S and Nano X
SEE ALSO: Investing in Litecoin and How it Works
SEE ALSO: 3 Smart Ways the Police Can Crackdown Cryptocurrency Criminals
The news of the dust attack sent shivers to the owners of Litecoin. It however was not clear if the infiltration was targeted to the community or to a single user who unsuspectingly grants access to a second wallet and it then goes viral.
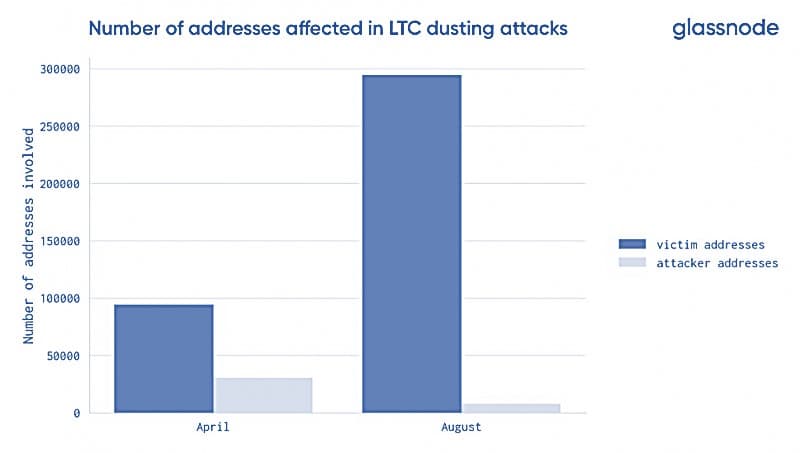
On August 15, 2019, Glassnode revealed in a tweet that 294,582 wallet addresses were affected by large-scale dusting attacks. A similar attack occurred months earlier in April affecting close to 100,000 wallets.
If the number of attacks more than doubled in subsequent months, the question now is, why are these attacks increasing?
In my opinion, the speed of embrace and the surge in prices has keep analysts and wallet providers busy on the business side, while losing their guard on security.
Owner of digital wallets should also admit some lax in securing their wallets as recommended by wallet providers. It only takes a slack for wallets to be compromised.
So, owners of cryptocurrencies in hot or cold wallets should take extra precautions since these assets are virtual and could disappear if handled carelessly.

SEE ALSO: How Does Proof-of-Stake Improve Proof-of-Work?
SEE ALSO: How to Create a Hashing Algorithm using Ethereum
SEE ALSO: How to Mine Ethereum and Earn Better than Bitcoin
Let’s examine dust in detail and how it works…
What is a Dust?
Dust refers to a small number of tokens or coins maliciously sent to random wallet addresses. It’s an amount so minute that many users may see it and ignore it. It’s similar to the pence or cents you often overlook in your bank balances.
Bitcoin, for example, the tiniest unit of it is 1 satoshi (which equals 0.00000001 BTC), so we can in this case say dust refers to a few hundred Satoshis.
In cryptocurrency exchanges, minute tokens reside in customers’ accounts following the execution of trading orders which is normal.
At the core of Bitcoin, dust is seen as whichever transaction output is less the transaction fees, which brings about the idea of dust limit.
Dust Limits
A dust limit is a leftover cryptocurrency not sufficient to complete another valid transaction. So, they are impossible to process.
The CEO of Bitrefill, Sergey Kotliar told Coindesk that raising the dust limits was a way to mitigate these attacks. Kotliar suggested that the limit be raised as proposed by Bitcoin Core Wallet. Most wallets have transaction caps of 546 sats (0.00000546 BTC or 8 cents)
Let’s look at this from a technical standpoint, the dust limit is computed based on the number of outputs & inputs which ordinarily rounds up to 546 satoshis for bitcoin transactions & 294 satoshis for native SegWit transactions.
If we look at this another way, dust infers that any typical transaction smaller than or same as 546 satoshis will be regarded as spam and it’s probable of being rejected by the authenticating nodes.
Note that dust holdings cannot be traced, but in exchanges like Binance, trading activities can convert these minute coins into the exchange’s native coin BNB.
How are Dusting Attacks Performed?
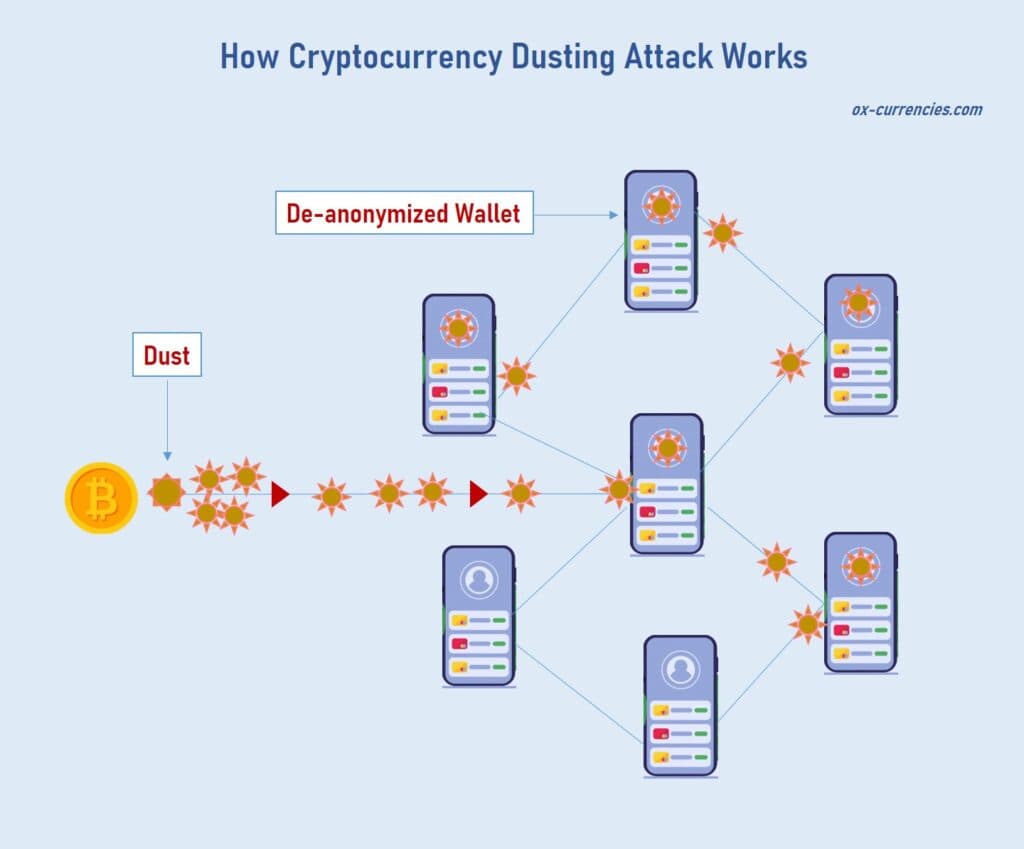
A dust attack is perfected when several wallet addresses are analyzed in a pool. The trick is that, for this type of attack to be successful, the dust pool must move for the attacker to establish a connection to unlock their privacy.
When the unsuspecting user spends out of the tainted or malicious coins, the dust attacker uses a malicious program to analyze the transaction which exposes the wallet’s transaction history.
This crypto tactic also offers a way to infiltrate a network by directing big batches of valueless transactions and downloading users’ data.
With this technique being prevalent in recent times, hackers have hijacked the tactics to wreak havoc, cryptocurrency owners now get targeted via phishing scams (email and SMS alerts).
Kotliar told Coindesk that users need not worry about their anonymity if they don’t consolidate their unspent transactions (UXTOs), however, some wallets automatically consolidate UXTOs for their owners.
SEE ALSO: 14 KEY Tips You Should Know Before Mining Bitcoin
SEE ALSO: 10 Best Cryptocurrency Exchanges in 2021
SEE ALSO: Best Hot and Cold Bitcoin Wallets
Dusting as a Tool
On the side of the law, mass dusting is employed by blockchain analytics establishments that research crypto dust for educational purposes or have agreements with governmental agencies.
Depending on who and how it is used, law enforcement does carry out dusting attacks to link a suspicious individual or group to a wallet address.
Most times, dusting is used to stress-test, where a huge amount of crypto dust is transferred within a short period to evaluate the bandwidth or throughout of a network.
Regardless of the purpose, mass dustings can be studied for various reasons, bad or good. The individual or group that performs the dusting attack and the faction that scrutinizes the results need not be the same.
As a result of being on the blockchain, people with the programs, time, and skills can study the crypto dust following an attack.
A criminal network could analyze a government’s dusting, likewise, a blockchain analytics establishment can analyze a gang’s dusting.
That is why “not all crypto dusting are seen as attacks”. The mass spreading of dust has as well been adopted to broadcast to crypto users, mainly by dolling out messages added to the crypto dust, the same way an email blast works.
Dusting can as well be used as a defensive instrument. For example, if a law enforcement agent is closing down on a big criminal organization syndicate, the syndicate is likely to dust several random wallets to distribute its dirty money all over to put the authorities off track.
As blockchain analytics improve, more countermeasures that would nip dusting in the bud are introduced. Some governments see the technology they use as proprietary and keep it a top-secret.
Financial Loss to Cryptocurrency Dusting
In as much as the exact amount lost to dusting cannot be fully ascertained as many cases are unreported, the consequential costs connected to dust attacks are usually more than the quantity of dust used.
Despite that the dust performed on a host of wallets may be insignificant, criminals still need to pay network charges to perform a dusting attack.
Should the limits or threshold on wallets be raised to put an end to these attacks? Analysts should weigh in on this idea.
Worried About Crypto Dusting Attacks?
Except you’re a whale (an individual with a large cryptocurrency reserve) what you’ll hear is that dust attacks are annoying, not something you should bother about.
A dusting of your wallet does not transfer control of your assets and anonymity.
New measures modern wallets and platforms are adopting has reduced significantly the usual concerns of dusting.
When you spot minute random transactions in your wallets, it’s simply a little dust.
Prevent Dusting Attacks
These are a few tips to prevent dusting attacks
- Use only Secured Exchanges to send and receive coins.
- Keep more than one wallet address and split your coins. Transact more with one.
- Verify monies sent to you by validating their source.
- Don’t mobilize suspicious coins in your wallet, report to the wallet provider.
- Own a Cold Wallet for better security.

Final Thoughts
Aside from dusting and other attacks that remove the anonymity of wallets, it is also valuable and safe to be aware of other cryptocurrency scams that are prevalent in the crypto space.
Read More