Since Ethereum made its debut in the cryptocurrency space in 2015, security, scalability, and energy efficiency have always been the long-term vision of the blockchain.
The Ethereum blockchain is currently based on a consensus mechanism known as Proof of Work (PoW) which relies on miners using their computer power and a huge amount of electricity to confirm transactions and add blocks to the blockchain.
Although this consensus mechanism was adopted from the alpha coin (Bitcoin), the Ethereum blockchain is now focusing on the Proof of Stake (PoS)which is a consensus mechanism designed not only to improve security and scalability but also energy efficiency.
Instead of relying on miners to add new blocks to the blockchain, it now relies on validators to stake their Ether (ETH) and take turns in proposing and attesting blocks.
These validators then receive rewards for their staking inputs computed accurately or may face penalties if they behave in ways that are not in the best interest of the blockchain network.
In this article, I will discuss extensively how these Ethereum validators are incentivized to stay active and honest.
Key Takeaways
• As a validator you are rewarded for proposing/attesting to blocks that are included in the chain. In layman’s terms, you are rewarded for actions that help the network reach a consensus.
• You can also receive a major or a minor penalty for inadvertent or malicious actions (or inactions) that hinder consensus.
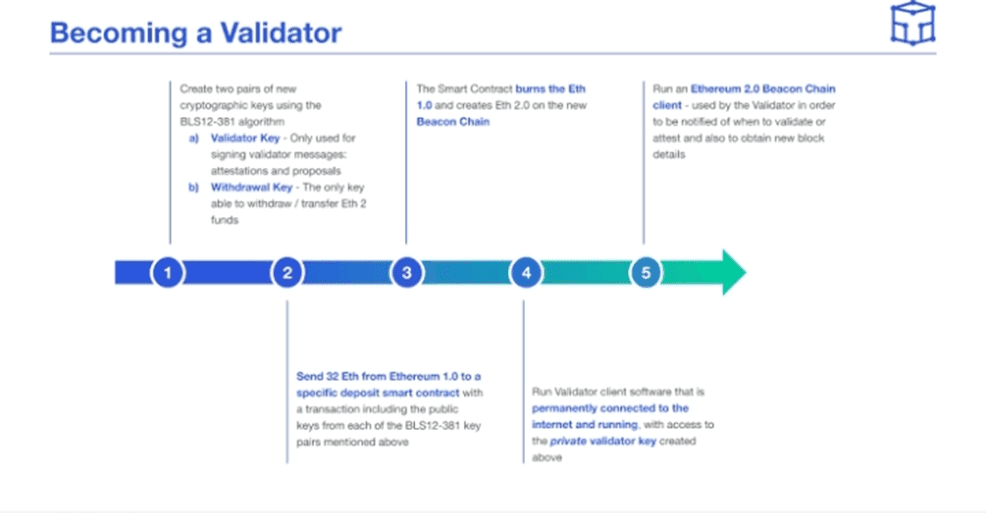
• Running an Ethereum validator requires 2 separate key pairs: the Validator key and the Withdrawal key.
• Ethereum 2.0 is currently live on the testnet, with holders already staking over 13 million ETH.
SEE ALSO: 5 Best Places To Stake Ethereum
SEE ALSO: How Often Are Rewards & Penalties Issued When Staking ETH?
Who is a Validator?
A validator refers to an individual running high-performance servers responsible for confirming transactions as well as proposing new blocks on Ethereum.
To become a validator, you must stake 32 ETH, which is subject to increase or decrease as you perform your assigned duties as a validator.
It is important to take note that a validator is relatively different from a miner on the legacy Ethereum chain because as a validator, you are called upon by the PoS protocol to propose and validate emerging blocks rather than compete for their generation as a miner in the legacy PoW method.
How Are Validators Incentivized To Stay Active and Honest?
To encourage validators to keep performing their tasks for the growth of the network, there are some sorts of incentives given to these validators to stay active and honest.
These incentives are known as rewards and there are 3 major classes of such rewards. They include; the Whistleblower reward, the Proposer reward, and the Attester reward.
Honest and active validators will be rewarded with new ETHs and transaction fees whereas dishonest or incompetent validators will have all or some of their staked ETH slashed.
Simply put, you maximize your rewards by providing the greatest benefit to the network as a whole.
Why Do Rewards Depend on the Total Number of Validators in the Network?
Block rewards are calculated using a sliding scale based on the total amount of ETH staked on the network. That is, if the total amount of ETH staked is low, the reward (interest rate) is high, but as the total stake rises, the reward (interest) paid out to each validator starts to fall.
Why use a sliding scale?
This is because there needs to be a minimum number of validators (and as a result a minimum amount of ETH staked) for the network to function properly.
So, to incentivize more validators to join, the interest rate must remain high until this minimum number is reached.
Although more validators are still encouraged to join (the more validators the more decentralized the network), they don’t have to do so (so that the interest rate can fall).
How Can I Become a Validator?
Any ETH holder can become a validator by simply staking 32 ETH. You can become a validator by using either of these two ways:
- Do It Yourself (DIY) Staking: Running a validator client (like Prysm, Nimbus, or Teku), Beacon, and Eth 2.0 node.
- Using a Staking Service: Staking services alleviate the technical facets of staking for users. There are custodial, semi-custodial, and non-custodial staking services available.
To become a validator, below are the steps that you need to take. They include;
Step 1: Install one of the previously listed Eth 2.0 validator clients.
Step 2: Get Ether
Step 3: Generate a validator public and private key pair (used for signing your claims as a validator).
Step 4: Start your validator client along with the Beacon chain. You can use your Beacon chain node or some existing public server.
Step 5: Make the ETH deposit (stake) to Eth1.
Step 6: Wait to get assigned as a validator. Once your validator client is up and running, you just have to wait for its activation. This might take hours or days due to a voting period in which new deposits are added to the running chain from other validators.
Step 7: Watch your validator create, vote, and attest for blocks as well as earn rewards!
Ethereum Staking Keys
To run an Ethereum validator, you need 2 different keypairs:
1. Validator Key
An online or hotkey that is used to sign the validator’s assigned duties.
2. Withdrawal Key
A key that is only used for transferring or withdrawing staked ETH. This key should be safely stored offline.
Note: Transfers and withdrawals will not be available until later phases of the network upgrade to Eth 2.0.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How many Ethereum validators are there?
Ethereum appears to be doing well based on the number of ETH validators out there according to the blockchain data. The number of network validators on Ethereum’s beacon chain is now over 350,000.
Q2. How much do ETH validators make?
Ethereum 2.0 validators will be earning up to 10% annually for staking 32 ETH needed to become a validator on the Ethereum 2.0 network.
SEE ALSO: A Beginner’s Guide to Mining Ethereum on Windows
SEE ALSO: 10 Best Blockchain Apps You Need To Know
Final Thoughts
The Ethereum protocol has reached another milestone as the number of Ethereum 2.0 validators has surpassed 350,000. As of the time of writing, the Ethereum 2.0 contract has over 13 million ether deposited which is worth billions of dollars.
The number of deposits and ETH validators keeps growing, but unfortunately, no one can guarantee when exactly the full transition to a PoS-based Ethereum 2.0 system will happen.
.
Read More