Hark Fork and Cardano’s History
A hard fork means when a radical change occurs in a blockchain’s protocol that there becomes a divergent path in that coin. Newer versions of the blockchain no longer accept the older version. So, an entirely new coin is created. Similar to a “chip off the old block”.
Cardano has gone through series of these changes and why has that changed the outlook of the ADA token?
We’ll explore that in detail, but let’s look at the the basics first.
Charles Hoskinson in September 2017, launched the Cardano network. The Mathematician and co-founder of Ethereum aimed to build a fast blockchain with high scalability.
The Network was based on the spectacular Ouroboros consensus mechanism.
Since its inception, the Cardano network had undergone series of hard forks which resulted in its remarkable development.
This article explains what a fork is, the types of the fork, the function, and how it has imparted the Cardano network.
What is a Fork?
Right from the onset, Bitcoin was created to be a decentralized virtual currency, a very competitive substitute for fiat currency.
After Bitcoin and Ethereum were created, many other digital currencies came into existence such as Bitcoin Cash, Bitcoin SV, Ethereum Classic, etc.
Interestingly, many of these currencies arose from a phenomenon now as Fork.
A fork occurs when a blockchain makes some changes to the protocol it uses to validate transactions.
Such changes are effected when the creators decide to change a basic component of the blockchain. It may be due to a division in the community or a major hack as in Bitcoin/Bitcoin Cash and Ethereum respectively.
SEE ALSO: ADA Staking: the Ultimate Guide to Cardano Staking
What is the Impact of a Fork?
The major effect of Fork on a cryptocurrency is that it causes price instabilities.
Two types of forks exist, soft fork and hard fork.
Soft Fork
A soft fork occurs if a blockchain is altered and its old nodes still validate new transactions.
At the same time, updated nodes will recognize the new transaction as invalid.
Nodes are computers used in the blockchain network. A successful soft fork has most of the hash power of the network.
Hard Fork
A hard fork on the other hand renders old nodes useless as they can not validate new transactions. Hence, updated nodes are required to validate new transactions.
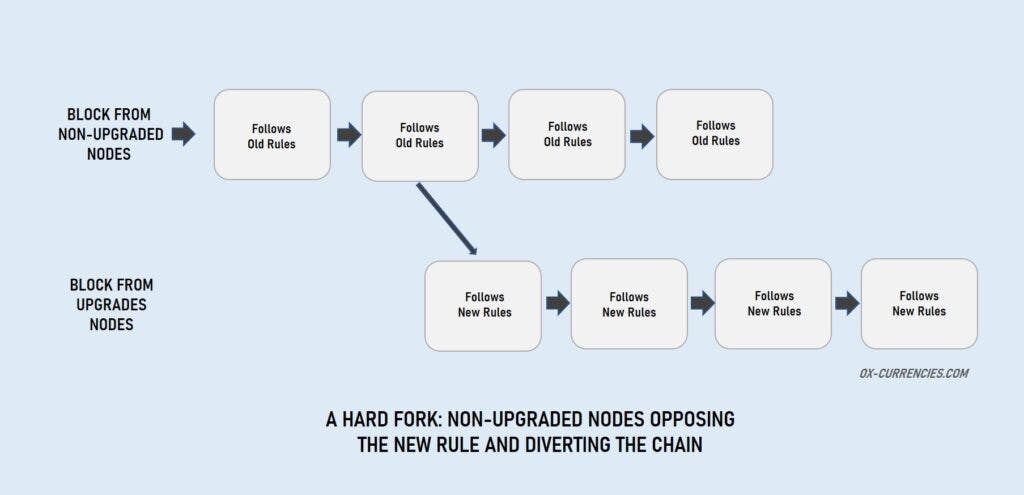
A successful hard fork needs both the users and developers to reach a consensus on whether the update is necessary or not.
If the majority agrees, then all nodes would be updated and the new rule will be implemented.
However, if there is a disparity in the network community, whereby some upgraded their nodes and others did not, this could lead to the same network producing two coins with different ledgers, one from the old nodes and the other from the updated nodes.
These two coins can coexist in two ways: one is when a coin’s operation is not affecting the other coin’s operation that is the two coins have a significant level of adoption and value in the community.
Two is where a coin is dominant with the other coin having a low adoption and value in the community.
In the case of the Ethereum network, the parent coin, Ethereum, outstandingly overperformed Ethereum Classic in adoption and value. However, Bitcoin Cash contends significantly with its parent coin, Bitcoin.
Cardano Hard Fork
Since Cardano’s launch in 2017, the coin has experienced a series of hard forks.
These hard fork changes helped it to achieve a lot of incredible feats.
Since we are considering Cardano, The following are the hard forks experienced by Cardano.
1. The Byron Era
It’s Foundation…
The Byron Era came in 2015 with the mindset of solving the logical puzzles (sustainability, scalability, and interoperability) troubling the blockchain network.
After weeks of immense studies, the Byron era marked the beginning of the first version of Cardano in September 2017.
This version enables users to purchase and sell the Cardano native coin, ADA, on a network based on the spectacular Ouroboros consensus mechanism.
ADA was named after Ada Lovelace, a revolutionary programmer. Ouroboros was built based on academic research with a level of security proven mathematically.
Daedalus and Yoroi wallets were both brought to the limelight during the era of Byron. They were built to enable daily and fast transactions. Byron era was the first fundamental technical development that was aimed at creating a community that would actively support the future of blockchain.
Today, Cardano developed into a worldwide community with its native coin, ADA, listed on more than 30 exchanges.
It has a significant average market capitalization which makes it ranked among the top cryptocurrency blockchain. These achievements show the Byron era was a success.
2. Shelly Era.
Decentralization…
The Shelly era came right after the Byron era.
During this era, the Cardano network experienced significant growth and development.
The Shelly era pursued a smooth and low-risk network experience. It initiates the decentralization of the Cardano network.
Previously, the Cardano community controlled the validation of transactions and other activities.
However, during the Shelly era, many nodes run independently by various participants resulting in the decentralization of the Cardano Blockchain network. Consequently, the level of Cardani security was improved.
Shelley era also introduced designation and incentives protocols. This allows users to stake their ADA into staking pools to participate in the validation of transactions on the network.
Therefore, users, according to proof of stake consensus, receive rewards for their loyal participation in the blockchain network.
This era depicts the natural growth of the blockchain network as it becomes more functional, rewarding, and beneficial to users. It also set the stage for the following forks.
3. Goguen
This Hard fork was focused on introducing the smart contract policy of the Cardano network.
It improved the serialization of the scripts and added trace and association scripts for the Uniswap contract. The API wallet was reorganized to solve the client-side errors of the wallet.
The Cardano community solved the scrolling bug in the contract card flow. They added tests based on a property for the example contracts. The FAQ content was also worked on.
4. Basho Era
Scaling
The Cardono’s Basho era was about the improvement of the scalability and interoperability of the blockchain network.
It was aimed at improving Cardano’s development and strength to adopt applications with a large volume of transactions.
It also introduced the use of sidechains. Sidechains are extra blockchains that can work simultaneously with the main blockchain thereby improving the capabilities of the network. They are used to initiate experimental components without altering the main blockchain’s security.
Generally, the Basho era improved the Cardona network in terms of scalability, security, resilience, and interoperability.
5. The Voltaire Era.
Governance
The Voltaire era aims at making the Cardano network a completely self-sustaining network. It introduced the treasury and voting policy which enables users to contribute to the future of the network via their voting and staking rights.
It helps to maintain the decentralization, staking, voting, and other improvements the network had experienced through the previous hard forks.
SEE ALSO: How to Mine Ethereum and Earn Better than Bitcoin
SEE ALSO: 5 Best Ethereum Wallets for Safe trading and Storage
SEE ALSO: Top 11 Best Cardano (ADA) Wallets for Staking & Storage
Final Thoughts
Not all hard forks result in a disparity in a blockchain community. The objective of a hard fork is to improve the network and make it more functional, secure, and easy to use.
Image credit: Money vector created by iuriimotov – www.freepik.com
Read More